Slit Lamp Exam: Uses, Procedure, and Advantages
Published on May 17th, 2024
 Australia
Australia
A slit lamp exam is a type of eye test performed by an optometrist or other eye care professionals to examine the inside of a patient’s eye. A slit lamp is a type of biomicroscope consisting of four main parts, the base, the patient support frame, the illumination arm and the viewing arm. A slit lamp test is used to check for signs of eye diseases and abnormalities as well as check the overall health of the eye. The types of eye diseases a slit lamp examination can detect include cataracts, glaucoma, corneal abrasions and dry eyes. Keep reading to learn more about how a slit lamp eye exam is performed and its advantages.
What is a Slit Lamp Exam?
A slit-lamp exam is a procedure performed in a standard eye test that assists optometrists in examining all parts of the eye and further inside the eye using a machine. Before a slit-lamp examination, the optometrist may need to dilate a patient's pupils to look closer at the back of the eye. A slit-lamp eye exam is performed using a microscope with a bright light and, according to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, is used to produce three-dimensional measurements and visualisation of the eye. A slit-lamp examination is used to assess overall eye health and observe the eyes for eye diseases and abnormalities such as cataracts, glaucoma and macular degeneration. According to HealthLink BC, a slit lamp exam typically takes between 5 and 10 minutes.
What is the Purpose of a Slit Lamp Exam?
The purpose of a slit lamp exam is to examine the inside of the eye to detect signs of eye disease and check overall eye health. According to the Cleveland Clinic, a slit lamp examination will look at a patient’s conjunctiva, sclera, cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina and optic nerve. This will allow the optometrist, or ophthalmologist, to check for various eye conditions and abnormalities such as glaucoma, corneal abrasions and cataracts.
How is a Slit Lamp Exam Performed?
The steps to perform a slit lamp exam, as described by the American Academy of Ophthalmology, includes positioning the patient, positioning the operator, focusing, illumination and magnification. These general steps and their definitions are listed below.
- Positioning the patient: The first step in a slit lamp exam is to ensure the patient is positioned properly. This involves making sure the patient is appropriately situated with their forehead and chin resting on the machine and that the surfaces have been thoroughly sanitised.
- Positioning the operator: The positioning of the operator involves having their dominant hand on the carriage and joysticks, with the other hand on the slit width adjustment knob. It is standard practice to examine the patient’s right eye first, then the left eye.
- Focusing: In the focusing stage, a light beam will be aimed at a point on the patient’s skin for coarse focusing and the operator will then slowly slide the carriage forward toward the patient.
- Illumination: Next, the eye care professional will adjust the intensity of the beam of light to ensure there is enough light to examine the patient but not too bright as to make them uncomfortable. Both the beam width and height can be adjusted to make measurements during the exam.
- Magnification: Magnification is controlled by a knob on the slit lamp machine. Lower power magnification is used for general examination and high power for the examination of fine structures of the eye.
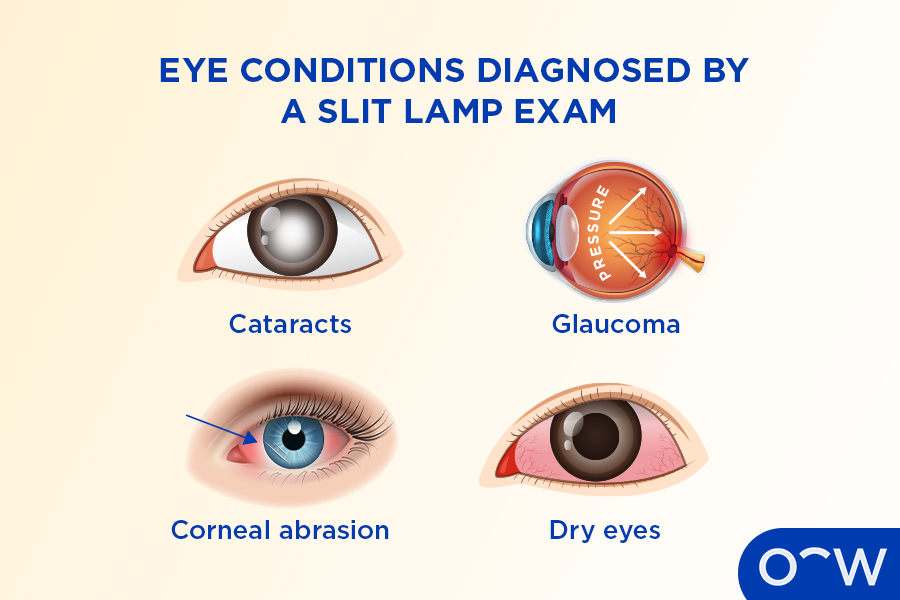
What Conditions and Eye Disorders Can a Slit Lamp Exam Diagnose?
A slit lamp exam is a key part in the diagnosis of many eye conditions and disorders. The eye conditions that an optometrist can check for in a slit lamp exam include cataracts, glaucoma, corneal abrasions and dry eyes. These conditions and their definitions are listed below.
- Cataracts: Cataracts are a clumping of protein in the eye’s lens which causes the lens to become cloudy instead of clear. In a slit lamp exam, the optometrist will look at the patient’s lens in order to diagnose cataracts.
- Glaucoma: Glaucoma is a term for a group of eye conditions or diseases in which damage to the optic nerve causes vision loss. A slit lamp exam gives an optometrist a detailed view of the optic nerve to diagnose glaucoma.
- Corneal abrasion: A corneal abrasion is a type of eye injury where the cornea sustains trauma which may be a scratch or tear. A slit lamp exam can allow the optometrist to check the eye for any damage to the cornea.
- Dry eyes: Dry eye is a common eye condition that can be described as a lack of tears produced or an inadequate quality of tears in the eyes. Examination of the cornea in a slit lamp exam can be used to identify dry eyes.

What are the Components of a Slit Lamp Microscope?
There are four main components of a slit lamp microscope, according to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, which each contain subcompartments. The four components of a slit lamp microscope are the base, the patient support frame, the illumination arm and the viewing arm, which are listed below.
- Base: The slit lamp base includes an adjustable table, power switch, intensity rheostat, locking carriage and joystick.
- Patient support frame: The patient support frame of a slit lamp includes a forehead band, chin rest, chin height adjustment knob, patient handles and canthus height indicator.
- Illumination arm: The illumination arm of the slit lamp includes a light source, illumination filters, beam height adjustment, slit illuminator, beam width adjustment and centre screw.
- Viewing arm: The slit lamp viewing arm includes oculars and a magnification control knob.
How Does a Slit Lamp Exam Differ from Other Eye Exams?
A slit lamp exam differs from other eye tests as it gives the eye care professional a closer look at the different structures inside the eye that cannot be done by simply looking with the naked eye. A slit lamp exam looks at the health of a patient's eye, whereas other tests such as a refraction test examine a patient’s vision.
What are the Advantages of a Slit Lamp Examination in Eye Healthcare?
The advantages of a slit lamp exam in eye care include detecting eye diseases and examining the overall health of the patient’s eye. > According to Medical News Today, a slit lamp exam can detect eye conditions and abnormalities such as cataracts, retinal detachment, macular degeneration, glaucoma, bleeding in the eye and damage to the sclera.


What are the Limitations of a Slit Lamp Examination?
There are few limitations of a slit lamp examination as it is a fundamental aspect of an eye test through which an optometrist can learn many key things about a patient’s eye health. The limitations of a slit lamp exam include the need to sanitise the machine between uses. After a slit lamp exam, an optometrist needs to thoroughly wipe the machine with alcohol before the next patient arrives, especially the chin rest and forehead band. While uncommon, patients may experience discomfort in a slit lamp exam if they have sensitivity to light, also known as photophobia.
Are There Specific Preparations or Precautions Patients Should Take Before a Slit Lamp Exam?
If a person has their eyes dilated for a slit lamp exam, then there are specific preparations and precautions a patient needs to take before a slit lamp exam. As the eyes will remain dilated for a while after the test, the patient will not be able to drive home and will need to organise transport home. If the patient’s eyes are not dilated, then there are no preparations needed for a slit lamp exam.
What can Eye Care Professionals Learn from the Results of a Slit Lamp Examination?
From the results of a slit lamp exam, an eye care professional can learn many things about their patient’s eyes and eye health. A slit lamp test allows an optometrist or another eye care professional to evaluate and diagnose a range of eye problems, diseases and other systemic diseases. A slit lamp eye exam is a crucial aspect of a standard eye test as it allows an optometrist to evaluate every anatomical compartment of the eye, according to the American Academy of Ophthalmology.
Read Slit Lamp Exam: Uses, Procedure, and Advantages in other Oscar Wylee regions and their languages.
 Australia
Australia




