UV Light: How It Works, Types, Effects and Protection
Published on September 26th, 2024
Updated on Decmber 16th, 2024
UV light or ultraviolet light is defined as radiation energy emitted from the sun and occurs in three forms, UVA, UVB and UVC. UVA measures around 315-400 nanometres (nm), UVB measures at 280-315 nm and UVC is 100-280 nm according to the World Health Organisation (WHO). UVA light rays infiltrate the deeper layer of the skin causing wrinkles and sun spots to develop and affect all structures of the eye. UVB rays are a medium wavelength that does not infiltrate past the superficial layers of the skin and is what leads to burning and delayed tanning. UVC is categorised as a short wavelength and is the most harmful form of UV radiation, however, it does not reach the earth’s surface as it is filtered by the atmosphere according to WHO. You can protect your eyes from the sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays by wearing glasses and/or sunglasses with UV 400, which helps to prevent UV light from damaging the eyes over time. If you’re wondering how UV light works, about the different types, effects and protection, continue reading for more in-depth information.
What is UV Light?
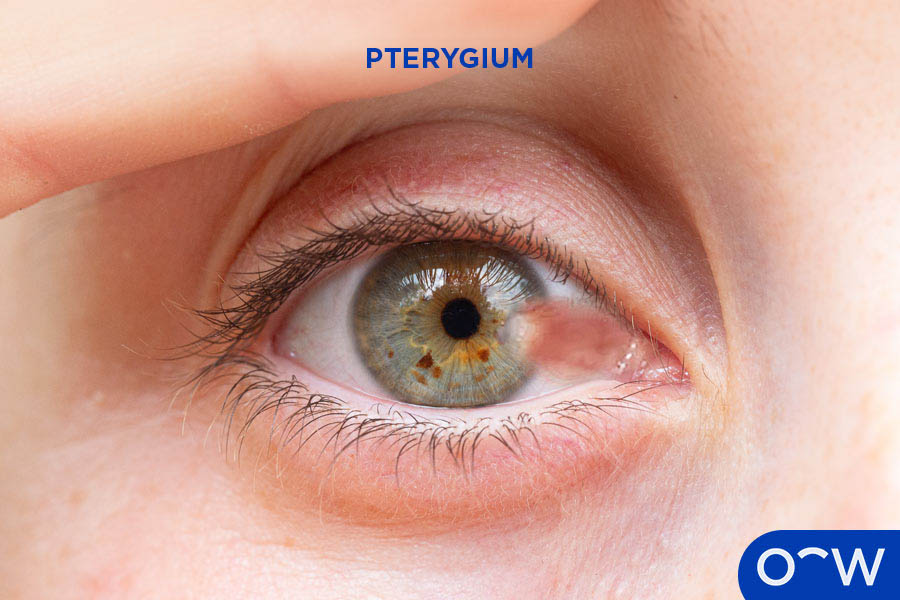
UV light, also known as ultraviolet light, is a form of radiation that comes from the sun. UV light is divided according to its different wavelengths with UVA being a long wavelength, UVB being a medium wavelength and UVC being a short wavelength. UVA light makes up around 95% of the radiation that reaches the earth’s surface and can enter into the deeper layers of the skin. UVB cannot penetrate the skin’s deeper layers but causes delayed tanning and burning and UVC light, while being the most harmful form, is blocked by the atmosphere and does not reach us. UV light can harm or change the proteins in the lens of the eye, increasing the risk of developing certain eye cancers and diseases. Long periods of unprotected exposure to ultraviolet light can bring on the risk of cataracts, pterygium, eyelid cancers, including basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, as well as poor vision according to the National Eye Institute.
How Does UV Light Work?
UV light works through its transmission by the sun and can be reflected off of certain surfaces such as snowy surfaces, bodies of water and through glare. Ultraviolet light occurs in three different wavelengths which are measured in nanometres with UVC being the shortest wavelength measured at 100-280 nm, UVB occurs in a medium wavelength of 280-315 nm and UVA is the longest wavelength of 315-400 nm according to the World Health Organisation.
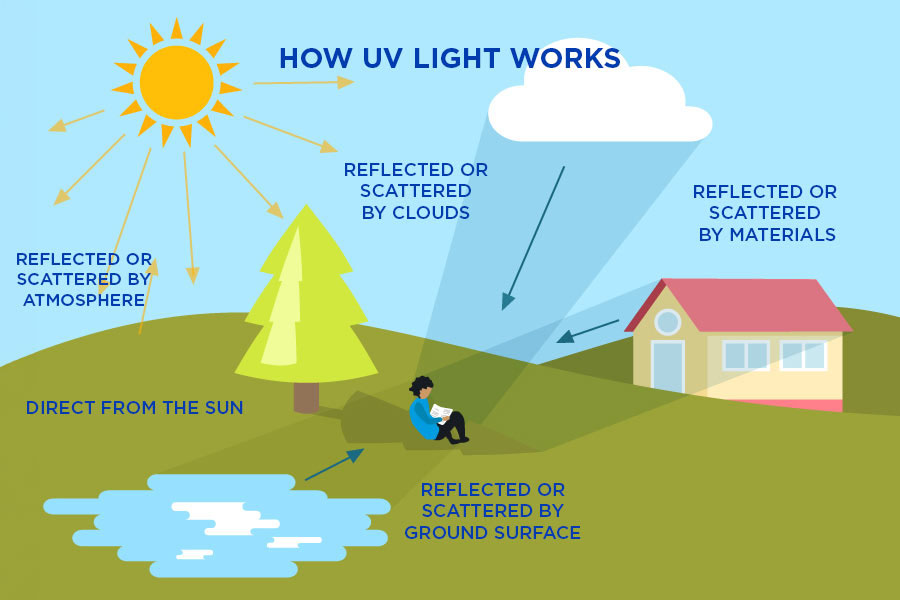

What are the Different Types of UV Light?
The different types of UV light are UVA, UVB and UVC, and are classified according to their respective wavelengths and the extent of their effect on human health. The different types of UV light are listed below.
- UVA: UVA light is a long wavelength that is measured at 315-400 nm and is able to reach the deeper layers of the skin. UVA light is what causes advanced skin ageing and wrinkling according to the World Health Organisation.
- VUB: UVB is a medium wavelength which is measured at 280-315 nm and while it does not reach past the superficial skin layers, it leads to delayed tanning and burning. UVB still contributes to the advanced ageing of individuals during unprotected exposure to UV light.
- UVC: UVC is the shortest wavelength and therefore the most harmful. However, UVC light is filtered by the atmosphere and does not reach us.
What are the Wavelengths of UV Light?
The wavelengths of UV light are UVA, UVB and UVC and range from long, medium to short wavelengths. The wavelengths of UV light are invisible to human eyes, however, can be seen by some insects such as bees according to NASA Science. The wavelengths of UV light are listed below.
| Types of UV Light | Wavelength Range | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| UVA | 315-400 nm | UVA is the longest wavelength, can pass through glass and clothing and the deeper layers of the skin. It contributes to advanced skin ageing and development of wrinkles on the skin. |
| UVB | 280-315 nm | UVB is a medium wavelength that can lead to tanning and burning of the skin’s outer layers. Unlike UVA, it is not able to penetrate the skin’s deeper layers. |
| UVC | 100-280 nm | UVC is characterised as the highest energy segment in the UV radiation spectrum. However, it does not pass through the earth’s atmosphere therefore, it does not reach us. |
What are the Natural Sources of UV light?
A natural source of UV light is the sun. The sun is a natural source of UV light and emits the complete spectrum of ultraviolet radiation according to NASA Science. Sunlight is made up of 400-700 nm of visible light and includes infrared radiation and UV radiation according to the International Agency for Research on Cancer.
How is UV Light Produced Artificially?
UV light is produced artificially through two ways that involves incandescent temperature or gas. UV light is produced either by heating a body to a temperature of over 2000 degrees celsius, also referred to as incandescent temperature according to Diffey (2002). The other way to produce artificial UV light is to pass an electric current through a gas. Vaporised mercury is typically used, according to Diffey (2002).
How Does UV Light Differ from Visible Light?
UV light differs from visible light due to the quantity of their energy and size of wavelengths. UV light differs from visible light as it is shorter than visible wavelengths and has more energy according to the UCAR Centre for Science and Education. Ultraviolet rays fall between visible light rays and X-rays within the electromagnetic spectrum. UV light is invisible to the human eye, however, some insects such as bees are able to see them.
Can You Block UV Light with UV Protection Sunglasses?
Yes, you can block UV light with UV protection sunglasses. Sunglasses with UV400 protection are able to prevent UV light from reaching the eyes by either absorbing or reflecting it. To ensure that UV protection sunglasses can effectively block UV light, they should have UV 400 sunglasses, which means the lenses can block up to 400 nm of UV light. All of our lenses at Oscar Wylee feature UV400 so you protect your eyes from UV light with both our optical glasses and sunglasses.


What are the Common Applications of UV Light in Healthcare?
The common applications of UV light in healthcare may include sterilisation and disinfection. Some healthcare practices may involve the use of UV light when eliminating germs on surfaces and instruments (Ramos., et al 2020). This was found to effectively remove inactive viruses and microorganisms such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, and vancomycin-resistant enterococci, according to the National Library of Medicine.
How is UV Light Used in Sterilisation and Disinfection?
UV light is used in sterilisation and disinfection by incorporating UVC light during cleaning protocols. UVC light is used to eliminate or immobilise microorganisms by harming their DNA according to Reed (2010). Upper-room ultraviolet germicidal irradiation (UVGI) is an established method of disinfection used especially in hospitals and health clinics to prevent the spread of infections according to the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention. UVGI can be utilised to disinfect water, air and surfaces.
What Role Does UV Light Play in Forensic Investigations?
UV plays an important role in forensic investigations as it can help reveal certain biological fluids that may be harder to see on different surfaces and fabrics. UV light can aid with the detection of perspiration, urine, saliva, blood, etc., as they reflect fluorescently when a source of UV light is shone onto them. Ultraviolet light may also be used to detect skin injuries according to Lynnerup, Hjalgrim and Eriksen (1995).
Is UV Light Used in Industrial Processes?
Yes, UV light is often used in industrial processes such as water and food disinfection, wastewater cleaning and the production of fluorescent materials. UV light can be used when killing any microbes found in water, meats and dairy products. It may also be utilised in the reuse of water through disinfection and cleaning and when creating materials such as paints and certain dyes according to the UN Academy.
What are the Effects of UV Light on Human Health?
The effects of UV light on human health are the increased risk of developing short-term and long-term complications for the skin and eyes. The effects of UV light on human health can include skin cancer, allergies, advanced ageing of the skin, sunburn, eye cancers and growths and cataracts. Long periods of unprotected exposure to the sources of UV light can accumulate damage to the skin and eyes over time but also result in harm even after short periods according to the Cancer Council. It is crucial to take preventative steps such as minimising time spent in the sun, using and reapplying sunscreen, wearing hats and using UV400 protection for your eyes. The effects of UV light on human health are listed below.
- Skin Cancer: Skin cancers are a potential effect of UV light on human health and can develop as a result of the impairment of the DNA in the skin cells. According to the American Skin Cancer Society, the majority of skin cancers are basal cell carcinomas.
- Allergies: Certain allergies can arise from exposure to the sun’s UV light over time, especially for those with more sensitive skin. UV light can modify a substance in the skin triggering the immune system to react and lead to skin inflammation according to the NHS.
- Advanced Skin Ageing: Advanced skin ageing can develop from unprotected exposure to UV light due to the UVA light penetrating the deeper layers of skin. This causes harm to the collagen fibres according to the Skin Cancer Foundation.
- Sunburn: Sunburns can come about after overexposure to the sun as the UV light causes damage to the outer layer of skin.
- Eye Cancers and Growths: Certain eye cancers and growths can be caused by excess UV light exposure, potentially from its effect on the skin’s DNA and the proteins in the eye.
- Cataracts: Cataracts can form in the eye due to the UV light passing through the lens, which leads to the proteins in the lens to separate and bunch together. This causes less light to be able to pass through the eye causing poor vision or loss of vision over time.

How Does UV Light Impact the Environment?
UV light impacts the environment as it can hinder photosynthesis in plants and algae. UV light affects phytoplankton especially, which accounts for around half of the atmosphere’s oxygen according to the Smithsonian Environmental Research Centre. However, UV light can also result in positive environmental outcomes such as cleaning water, and enabling more access to light for aquatic photosynthetic organisms.
What Measures Can be Taken to Protect Against Harmful UV Exposure?
The measures that can be taken to protect against harmful UV exposure include wearing sunscreen, avoiding prolonged UV light exposure and wearing a hat. The measures that can be taken to protect against harmful UV exposure are listed below.
- Wear Sunscreen: Wearing sunscreen can help protect the skin from UV light damage as they can either contain physical or chemical blockers. Physical blockers possess titanium dioxide or zinc oxide which sits on the skin’s surface and reflects the UV rays according to the MD Cancer Research Centre. Chemical blockers in some sunscreens work by creating a thin protective film that can absorb the ultraviolet radiation before it infiltrates the skin.
- Avoid Prolonged UV Light Exposure: Avoid prolonged UV light exposure to prevent the risk of short-term and long-term damage to the eyes and skin. It may be helpful to find shade when spending time outdoors every now and then or to spend timed periods outdoors.
- Wear a Hat: Wear a hat when outdoors to shield your face and eyes from the sun. This can help reduce the risk of excessive exposure to UV light.
Do Glasses Provide UV Protection?
Yes, glasses can provide UV protection. Glasses that have UV protection lenses are equipped to either block or absorb the UV light rays so they don’t reach the eyes. It is important to ensure with the optometrist or retail member if your glasses or sunglasses feature UV 400 protection as this can guarantee complete UV protection. In some cases, UV blocking glasses may only offer up to 380 nm. According to the Cancer Council, the required amount for UV protection is between 190 nm and 400 nm, therefore, making it permissible for UV protection to be less than 400 nm. Here at Oscar Wylee, all lenses are equipped with UV 400 protection to ensure optimal protection for both optical glasses and sunglasses.



