Tonometry Test: Importance, Procedure, Types and Results
Published on April 29th, 2024
 Australia
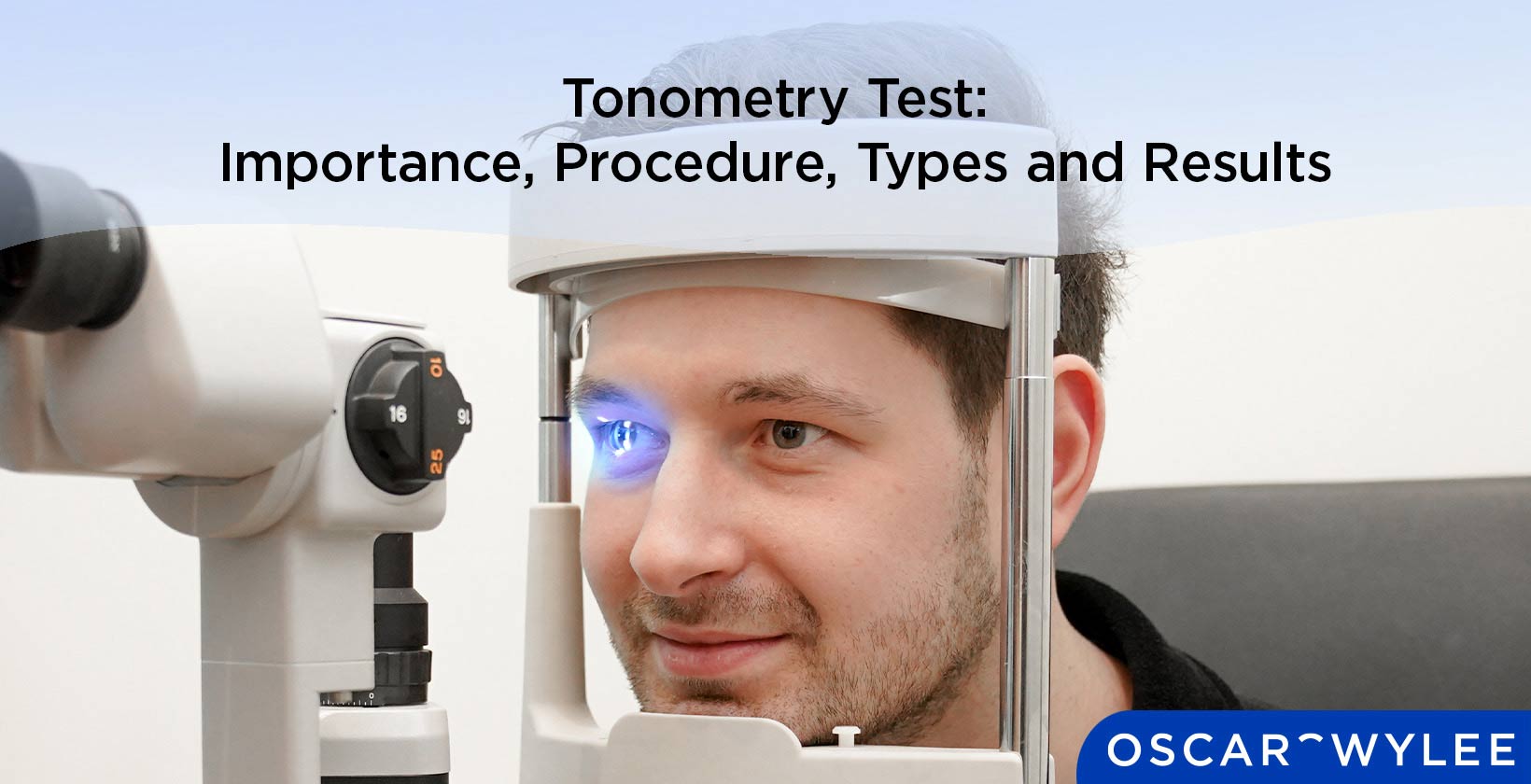
Australia A tonometry test is an eye testing procedure in which eye pressure, also known as intraocular pressure (IOP), is tested. A tonometry test is a hugely beneficial procedure to have, as it can detect glaucoma, an eye condition that can lead to vision loss. There are several types of tonometry tests including electronic indentation tonometry, applanation (Goldmann) tonometry and non-contact tonometry. A tonometry test will be performed by an optometrist or ophthalmologist, and is generally a simple, painfree procedure. At Oscar Wylee, a tonometry test is performed as part of a regular eye test, which is bulk billed for eligible Medicare cardholders. Keep reading to learn more about a tonometry test.
What is the Importance of a Tonometry Test?
A tonometry test is an important eye testing procedure as it checks eye pressure, also known as intraocular eye pressure (IOP). An abnormality, such as an increase in eye pressure, can lead to issues within the eye and is a major risk factor for the eye condition glaucoma. A tonometry test is therefore hugely important in checking whether a person is at risk, or has glaucoma. A tonometry test is also useful in assessing how well glaucoma treatment is working.


How Does the Tonometry Test Work?
The way a tonometry test works will be determined by the method or type of tonometry test an optometrist chooses to use. There are several types of tonometry tests that can assess a person’s eye pressure including applanation tonometry, indentation tonometry and non-contact tonometry, according to HealthLink BC. Applanation works by using a small disk to flatten an area of the cornea. Indentation tonometry works by using a small rounded tool to make a small ident in the cornea. A non-contact tonometry test works by using small puffs of air from a machine to flatten the cornea.
What to Expect During the Tonometry Test?
What to expect during a tonometry test will be determined by which method or which type of tonometry test is used. A non-contact tonometry test will not touch the eye and shouldn’t be painful, but may feel like a small amount of pressure. An electronic indentation or applanation tonometry test are contact tonometry tests that use force to flatten the cornea. An optometrist may use numbing eye drops so a patient does not feel the force from an electronic or applanation tonometry test.
Does the Tonometry Test Hurt?
A tonometry test should not hurt. Electronic indentation or applanation tonometry involves an instrument touching the eye that may cause mild discomfort. An optometrist may choose to use numbing eye drops for contact tonometry tests to lessen discomfort. Non-contact tonometry is available as an alternative. Non-contact tonometry should not hurt, but patients may feel some pressure from the puffs of air directed into the eye.
How Often Should You Have an Eye Test?
A person should have a regular eye test at least once every 1-2 years. An optometrist will advise a patient if they need more frequent eye tests. Factors that may inform how often a person gets an eye test include age or eye conditions that need monitoring, such as glaucoma. A person will typically get a tonometry test as part of a regular eye test.
What are the Types of Tonometry Tests?
There are several types of tonometry tests that can be undertaken to measure intraocular pressure, including electronic indentation tonometry, applanation (Goldmann) tonometry and non-contact tonometry. The types of tonometry tests are listed below.
- Electronic Indentation Tonometry: Electronic tonometry refers to a tonometry test that uses a tool with a rounded tip, placed onto the cornea, to measure intraocular pressure.
- Applanation (Goldmann) Tonometry: Applanation (Goldmann) tonometry refers to a tonometry test that uses a small disk to flatten an area of the cornea which gives an indication of intraocular pressure.
- Non-contact tonometry: Non-contact tonometry refers to a tonometry test in which puffs of air are directed onto the cornea until it flattens, to help measure intraocular pressure without needing to touch the eye.
1. Electronic Indentation Tonometry
Electronic indentation tonometry refers to a tonometry test in which an optometrist will place the rounded tip of a tool onto the cornea with the results sent to a computer, according to My Health Alberta. The principle behind indentation tonometry is that an object will sink further into a soft eye than a hard eye, according to the American Academy of Ophthalmology. A hard eye can be caused by an increase in intraocular pressure. Numbing eye drops may be used so a patient does not feel the force during an electronic tonometry test.
2. Applanation (Goldmann) Tonometry
Applanation tonometry refers to a tonometry test using a small disk to flatten an area of the cornea. The principle behind applanation tonometry is based on Imbert–Fick law, which theorises that the pressure inside a sphere can be measured by how much force it takes to flatten certain areas of the sphere, according to Aziz and Friedman in Tonometers-which one should I use? In applanation tonometry, a small disk is used to flatten an area of the cornea. According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, intraocular pressure is then determined by the applanation force of the area of the cornea that is flattened. A person may be given numbing eye drops for this test so they do not feel the force of the test.
3. Non-contact Tonometry
Non-contact tonometry refers to a tonometry test that uses a small puff of air from a machine to test intraocular pressure, without needing to touch the eye directly. The air is directed into the eye until the cornea flattens. According to MyHealth Alberta, non-contact tonometry is not the most accurate test of intraocular pressure but is a quick way of seeing if a person has high ocular pressure.
How Long Does it Take to get the Results of a Tonometry Test?
The results of a tonometry test should be immediate. For electronic indentation tonometry tests, the results will be sent to a computer as they come through. An optometrist will generally be able to tell the results of non-contact tonometry and electronic indentation tonometry immediately after tests are completed.
What is an Example of a Tonometry Test Result?
Eye pressure is measured in millimetres of mercury, according to the American Academy of Ophthalmology and is abbreviated to mm Hg. According to Mount Sinai Medical Centre, the normal eye pressure range is within 10 - 21 mm Hg.
How Accurate is the Tonometry Test?
Certain types of tonometry tests are more accurate at measuring eye pressure than others, with the applanation (Goldmann) tonometry test considered the most accurate, according to Glaucoma Australia. Applanation tonometry testing involves a tool that flattens the cornea to measure eye pressure.
What Happens if IOP is Too High?
If intraocular pressure (IOP) is too high, it may lead to ocular hypertension and eye conditions such as glaucoma. Ocular hypertension refers to high intraocular pressure, caused by fluid not draining from the eye properly. Ocular hypertension does not mean a person has glaucoma but they may be considered more at risk of developing it. Glaucoma is an eye condition in which damage to the optic nerve causes vision loss. Glaucoma can be caused by high intraocular pressure.


What are the Benefits of a Tonometry Test?
The benefits of a tonometry test are that it measures intraocular pressure (IOP) and can detect glaucoma. Glaucoma is an eye condition in which high intraocular pressure causes damage to the optic nerve, which leads to vision loss. A tonometry test is a hugely important test in diagnosing glaucoma, as well as detecting who may be at risk for glaucoma due to elevated intraocular pressure.
What are the Downsides of the Tonometry Test?
There are a few downsides to a tonometry test, as they are a good tool for checking intraocular pressure and can help detect glaucoma. It is generally a pain-free procedure, with mild discomfort. An optometrist may provide numbing eye drops so a patient doesn't feel this discomfort. According to HealthLink BC, the eye may feel scratchy after a contact tonometry test, but this should go away in 24 hours.
Is a Tonometry Test only used to Diagnose Glaucoma?
A tonometry test is performed to assess a person’s intraocular pressure as a way to screen for glaucoma. While tonometry is used to diagnose glaucoma, it also measures how well glaucoma treatment is working, according to Medline Plus. Glaucoma refers to a group of eye conditions or diseases in which damage to the optic nerve causes vision loss.
Is a Tonometry Test Expensive?
At Oscar Wylee, a tonometry test is a standard part of a regular eye test which is offered at a bulk billed price for eligible Medicare cardholders.
Who are the Eye Care Professionals who Perform Tonometry Tests?
The eye care professionals who perform tonometry tests include optical assistant, optometrists and ophthalmologists. It is more common for a trained optical assistant to perform a tonometry test as it is part of the pre-testing routine before the patient sees the optometrist. The machine is also not typically located in the optometrist's room. Optometrists and ophthalmologists may also perform tonometry tests if the need arises.
Does Oscar Wylee Offer a Tonometry Test?
Yes, Oscar Wylee offers a tonometry test to patients who book an eye test. At the start of every Oscar Wylee eye test, an optical dispenser or member of our retail staff will perform a non-contact tonometry test to assess intraocular pressure. After the tonometry test, the patient will be passed along to an Oscar Wylee optometrist to continue their eye test appointment.
What is the Difference Between a Tonometry Test and a Tomography Test?
The difference between a tonometry test and a tomography test is that they are performed to assess different aspects of the eye. According to the Cleveland Clinic, a tomography test is a kind of digital imaging that captures a cross-section of the optic nerve or retina. On the other hand, a tonometry test is performed by an optometrist or optical dispenser to assess a patient’s intraocular pressure.


Read Tonometry Test: Importance, Procedure, Types and Results in other Oscar Wylee regions and their languages.
 Australia
Australia