Aqueous Humour: Function, Location, What Affects It and How to Keep It Healthy
Published on June 2nd, 2024
The aqueous humour is a transparent fluid located in the space between the cornea and the lens, also known as the anterior chamber. The aqueous humour has several functions including keeping eye pressure, keeping the shape of the eye and providing the eye with nutrients. The aqueous humour works by first being made by the ciliary body and then flowing into the anterior chamber. The fluid then flows through the trabecular meshwork and is drained. Issues with how the aqueous humour flows and drains can lead to an increase in eye pressure, which raises the risk of glaucoma. Glaucoma refers to a group of eye conditions that leads to vision loss due to damage to the optic nerve. It is important to take care of the eyes, including the aqueous humour, so the risk of developing high intraocular pressure and subsequent eye problems is reduced. The ways to take care of the eyes and in turn the aqueous humour is by booking regular eye tests, eating a balanced, healthy diet, regularly exercising and stopping smoking. Keep reading to learn more about the aqueous humour, its function, location, what affects it and how to keep it healthy.
What is the Aqueous Humour?
The aqueous humour is a transparent fluid that fills the space between the cornea and the lens. The main function of the aqueous humour is to keep the eye pressurised and in shape, whilst also providing nutrients. According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, the eye constantly produces a small amount of aqueous humour which in equal parts flows out or drains from a structure called the trabecular meshwork. The ciliary body, a part of the eye attached to the iris, makes the aqueous humour, which then flows into the eye through the pupil and out through a structure called the trabecular network, according to the New York Presbyterian Health Library. The aqueous humour resembles blood plasma in composition, according to Britannica.
What is the Function of the Aqueous Humour?
The aqueous humour has several functions including keeping eye pressure, keeping the shape of the eye and providing the eye with nutrients. One of the main functions of aqueous humour is to provide shape and pressurisation for the eye. According to the Cleveland Clinic, eye pressure is maintained when the same amount of aqueous fluid enters and leaves the eye. According to Britannica, the aqueous humour provides a variety of nutrients to the structures in the eye that lack a direct blood supply, including the lens and also drains waste from these structures.
How Does the Aqueous Humour Work?
The aqueous humour works through a series of structures in the eye including the ciliary body, trabecular meshwork and drainage canal, all working to drain the aqueous humour of the eye and keep the flow of fluid going as the ciliary body creates it. According to the BrightFocus Organisation, aqueous humour is made by the ciliary body and then flows into the anterior chamber. The fluid then flows through the trabecular meshwork, which is a spongy tissue at the front of the eye and is drained.
Where is the Aqueous Humour Found?
The aqueous humour can be found between the cornea and the lens, also known as the anterior chamber of the eye. The cornea is the transparent layer that covers the eye. The lens is a clear structure behind the iris that helps direct light onto the retina.
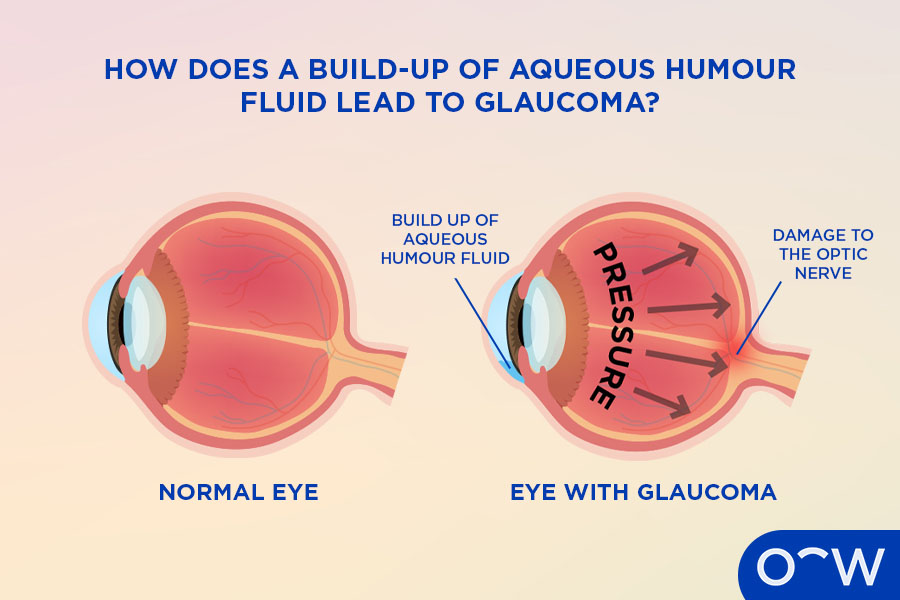
How Does a Build-Up of Aqueous Humour Lead to Glaucoma?
A build-up of aqueous humour may lead to glaucoma, as this can increase intraocular pressure and damage the optic nerve. Glaucoma refers to a group of eye conditions that leads to vision loss due to damage to the optic nerve. Glaucoma can be caused by high intraocular pressure, which refers to the pressure inside the eyeball being too high. According to the paper, Open Angle Glaucoma by Mahabadi, Zeppieri and Tripathy, primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) is the most common type of glaucoma caused by issues with the aqueous humour and is characterised by the aqueous humour being resistant to drainage via in the trabecular meshwork. The aqueous humour is typically created by the ciliary body and drained out of the eye via the trabecular meshwork. If there is an issue with the drainage, aqueous fluid can build up and raise eye pressure.

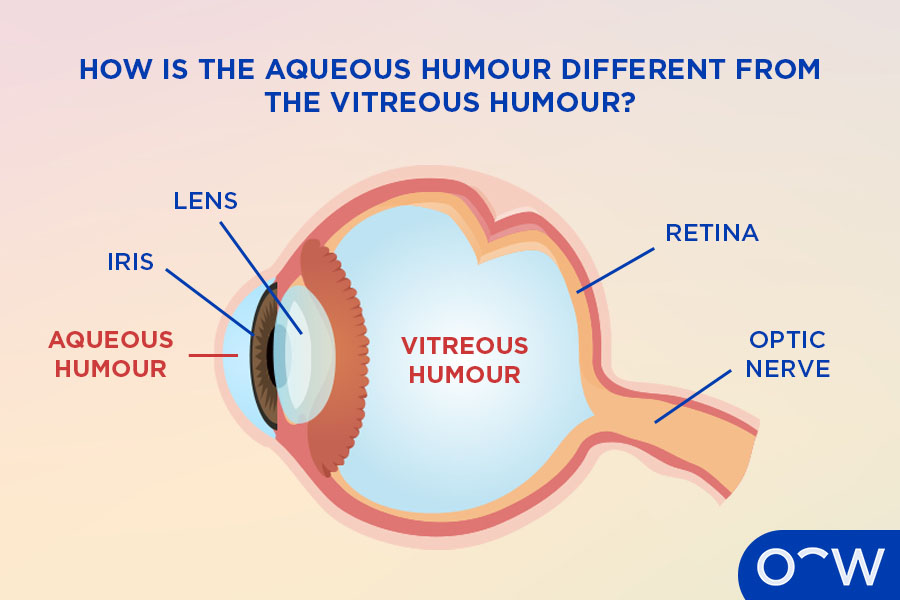
How is the Aqueous Humour Different from the Vitreous Humour?
The aqueous humour and the vitreous humour are both types of fluid that fill the eye and play important roles in maintaining eye health, with the main differences between them being their location and composition. The vitreous humour is a clear, gel-like substance located behind the lens and in front of the retina in the vitreous cavity. The vitreous humour has several main functions including maintaining the shape of the eye, vision clarity, maintaining oxygen gradient and shock absorption. The aqueous humour is located in the anterior chamber of the eye and is responsible for providing the eye with nutrients, taking away waste products and keeping the eye pressurised and in shape. The aqueous humour and vitreous humour are both made of mostly water, however, the aqueous humour is also composed of amino acids and electrolytes, lactic and ascorbic acids, whereas the vitreous humour has collagen, proteins and glucose.

Does the Quality of Aqueous Humour Deteriorate as You Age?
The quality of the aqueous humour does not necessarily deteriorate as you age, however, studies have shown that the structures that drain the aqueous humour such as the trabecular meshwork may be affected with age. According to the paper, Changes in aqueous humour dynamics with age and glaucoma by Gabelt and Kaufman, age can contribute to an accumulation of extracellular material in the trabecular meshwork and ciliary muscle, which can lead to a reduction in the drainage of aqueous fluid from the eye. This may lead to increased eye pressure and put a person at risk for eye conditions such as glaucoma.
How Can You Keep the Aqueous Humour Healthy?
The ways to keep the aqueous humour healthy revolve around taking care of the eyes in general, which will benefit the aqueous humour. The ways to take care of eye health include booking regular eye tests, eating a balanced and healthy diet, regularly exercising and stopping smoking. The ways to keep the aqueous humour healthy are listed below.
- Booking regular eye tests: Booking regular eye tests is an important step in taking care of the eyes. A regular eye test allows an optometrist to assess vision and examine the structures of the eyes for possible eye conditions or diseases. It is generally recommended that people have an eye test every 1-2 years, however, the exact frequency will depend upon the specific patient, their underlying health conditions and what their optometrist has recommended.
- Eating a balanced and healthy diet: Eating a balanced and healthy diet, which can include whole foods, fruits and vegetables, healthy fats and proteins, is very beneficial for overall health, including the health of the eyes. A balanced, healthy diet ensures the body gets the nutrients it needs to function properly and can also reduce the risk of health conditions such as heart disease. Certain foods have specific benefits for the eye, helping to reduce the risk of vision issues such as cataracts. According to Havard Health, vitamins, A, C, E, zinc and omega-3 fatty acids, may help maintain good eye health.
- Regularly exercising: Regularly exercising is an important way to care for overall health, including the eye. Regular exercise can include cardio such as running and swimming, walking, lifting weights and pilates. Regular physical activity reduces the risk of health conditions such as cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes, which can have an impact on eye health.
- Stop smoking: Stopping smoking is an important step in maintaining eye health and in turn the health of the aqueous humour. Smoking is proven to increase the likelihood of developing cataracts between two and three times, according to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). People who smoke are also up to four times more likely to develop age-related macular degeneration (AMD) than non-smokers.
How Does Aqueous Humour Maintain Eye Pressure?
The aqueous humour does not maintain eye pressure alone. Eye pressure is maintained when the aqueous humour is produced and drained in equal measure by various structures in the eye. According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, the ciliary body constantly produces a small amount of aqueous humour which in equal parts flows out or drains from a structure called the trabecular meshwork. If the aqueous humour cannot drain properly, this will impact the pressure in the eye.
What Stimulates Aqueous Humour Production?
The ciliary body is the structure that produces the aqueous humour. According to the Mount Sinai Health Organisation, the ciliary body is an extension of the iris, the coloured part of the eye, responsible for aqueous humour production as well as accommodation. Accommodation is the process by which a muscle called the ciliary muscle changes the shape of the lens to help the eye focus on an object.
What Causes Poor Drainage of the Aqueous Humour?
Poor drainage of the aqueous humour is related to issues with the trabecular meshwork, which is the spongy tissue found near the cornea, where the aqueous humour drains out. Issues with the trabecular network can often be related to age. According to the paper, Changes in aqueous humour dynamics with age and glaucoma by Gabelt and Kaufman, as a person ages, there may be an accumulation of extracellular material in the trabecular meshwork, affecting how well aqueous fluid drains from the eye. Issues with the trabecular meshwork may also occur in younger patients, related to abnormal development of the meshwork leading to it not functioning properly, according to the BrightFocus Foundation.
Can a Tonometry Test Determine the Health of Your Aqueous Humour?
Yes, a tonometry test can indicate the health of the aqueous humour and how well it serves its function of maintaining eye pressure. A tonometry test is a type of eye test that measures eye pressure. As the aqueous humour is responsible for maintaining eye pressure, a tonometry test can be a way to assess how well the aqueous humour is working. A tonometry test works by flattening the cornea. The harder it is to flatten the cornea, or the more resistance there is, the higher the eye pressure is. There are several types of tonometry tests, both contact and non-contact. One of the most common is non-contact tonometry where a puff of air is blown onto the cornea to flatten it.
Is Eye Surgery the Only Treatment Option for Issues Related to the Aqueous Humour?
No, eye surgery is not the only treatment option for issues related to the aqueous humour. Glaucoma is the main eye condition that can arise due to issues with the aqueous humour and how it drains. Glaucoma refers to a group of eye conditions in which damage to the optic nerve leads to vision loss. This optic nerve damage can occur due to high ocular pressure. Eye surgery can be used to help relieve this high eye pressure and stop the condition from worsening. A surgery called a trabeculectomy may help to relieve eye pressure by helping the aqueous humour drain from the eye. A trabeculectomy involves creating an opening in the top of the eye to help fluid drain, according to the National Eye Institute. Eye surgery is one of several treatments for glaucoma, however, medicine such as eye drops and laser surgery are also available.