Retina: Anatomy, Function, and Related Eye Conditions
Published on March 4th, 2024
The retina is a layer of light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye that is responsible for turning the light the eye receives into electrical signals, that are then sent to the brain. These signals are then interpreted by the brain as a visual picture. The anatomy of the retina is complex, involving cone cells, the fovea, the macular, rod cells, photoreceptors and the peripheral retina. There are also several layers to the retina, including Inner Limiting Membrane, Nerve Fiber Layer, Ganglion Cell Layer, Inner Plexiform Layer, Inner Nuclear Layer, Outer Plexiform Layer, Outer Nuclear Layer, Outer Limiting Membrane, Photoreceptor Layer and the Retinal Pigmented Epithelium. The retina is an important part of the eye, playing a crucial role in ensuring a person can see properly, therefore it is important to take care of the retina to limit the chances of developing certain retina-related eye problems. Retina-related eye problems include eye floaters, diabetic retinopathy, retinitis pigmentosa, retinoblastoma, posterior vitreous detachment, retinal detachment, macular pucker, macular hole, retinal vein occlusion, age-related macular degeneration. Ways to take care of the retina include attending eye tests with an optometrist, eating a healthy and balanced diet, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking.
What is the Retina?
The retina is a layer of light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. The purpose of the retina is to take the light that the eye sees and change this light into electrical signals that can then be transmitted to the brain, which can then perceive a visual picture, according to Nguyen KH, Patel BC, Tadi P. in Anatomy, Head and Neck: Eye Retina.
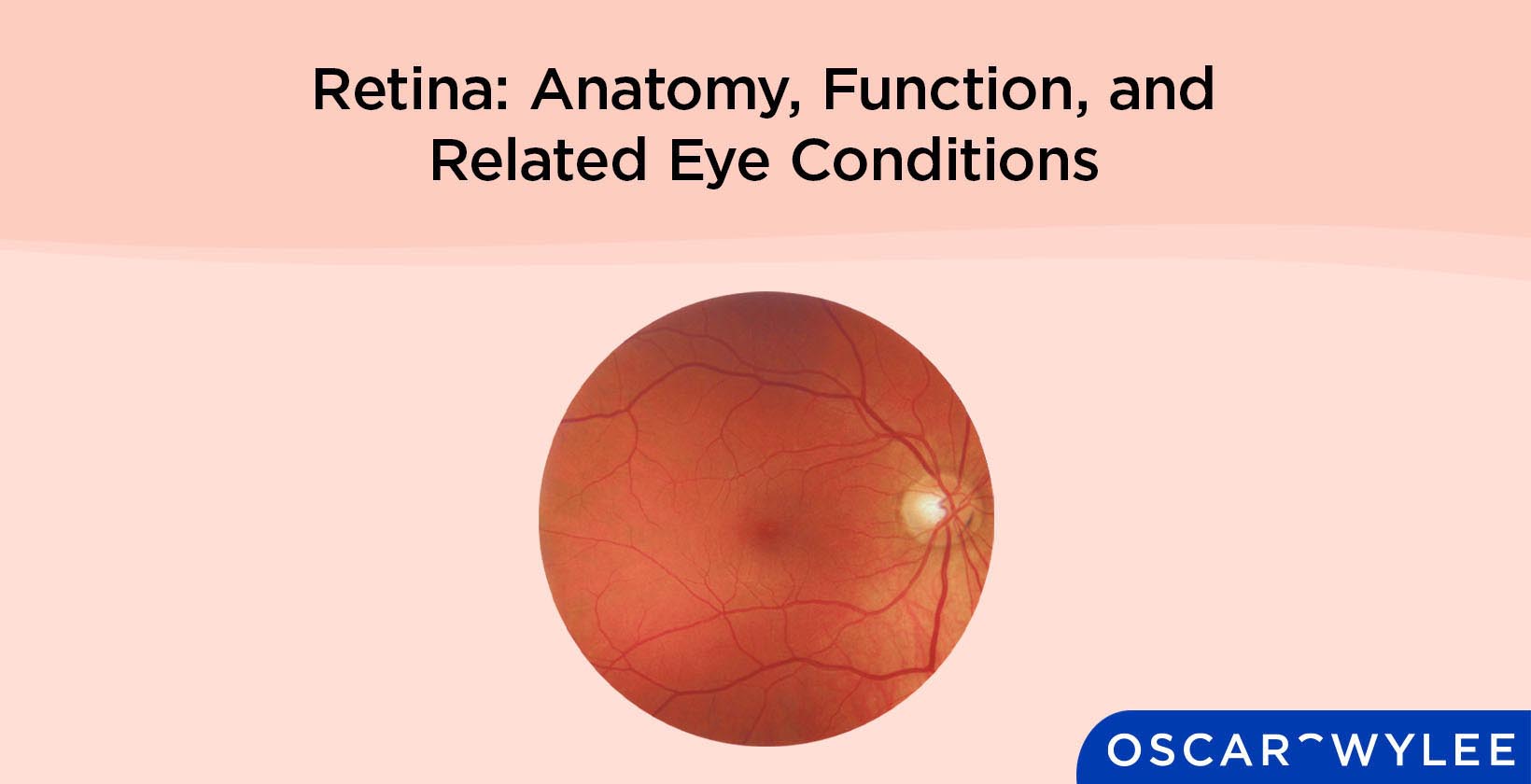
What is the Structure of the Retina?
The structure of the retina is complex and involves several parts such as the photoreceptor cells, the macula, and the fovea. Photoreceptor cells are one of the most crucial parts of the retina structure, as they convert light into electrical signals. According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, there are two types of photoreceptor cells; cones, which provide colour vision, and rods, which are sensitive to light levels. Cone cells are located in the macula. The macula is located in the middle of the retina and is responsible for processing central vision. Another part of the retina anatomy is the fovea. The fovea is a depression in the macula, responsible for visual acuity.


What is the Retina Made Of?
The retina is made up of several different types of cells. According to Mahabadi N, Al Khalili Y in the paper Neuroanatomy, Retina the three types of cells that make up the retina are neuronal cells, glial cells and photoreceptor cells, which include rod and cone cells.
What are the Layers of the Retina?
The anatomy of the retina is complex, involving several layers. The layers of the retina include the Inner Limiting Membrane, Nerve Fibre Layer, Ganglion Cell Layer, Inner Plexiform Layer, Inner Nuclear Layer, Outer Plexiform Layer, Outer Nuclear Layer, Outer Limiting Membrane, Photoreceptor Layer and the Retinal Pigmented Epithelium.
What is the Color of the Retina?
The retina is typically an orange colour.
Where is the Retina Located?
The retina is located in the back of the eye. According to Nguyen KH, Patel BC, Tadi P. in the paper Anatomy, Head and Neck: Eye Retina, the retina is located in the posterior segment of the eye, forming an innermost boundary for other layers of the eye.
What is the Function of the Retina in the Eye?
The function of the retina in the eye is to change the light that the eye receives into electrical signals. These signs are then transmitted to the brain via the optic nerve, where it creates images. The main retina function is to help a person see.
How do the Retina and Optic Nerve Work Together?
The optic nerve and the retina work together to help transmit visual information to the brain so a person can see. The retina takes in light that the eye sees and turns this into electrical signals. The optic nerve then takes these signals to the brain. The optic nerve is a nerve located at the back of the eye, connected to the brain.


What are the Parts of the Eye Associated with the Retina?
Several parts of the eye’s anatomy are associated with and make up the retina, including cones, the fovea, the macula, rods, photoreceptors and the peripheral retina. The parts of the eye associated with the retina are listed below.
- Cones: Cones or cone cells are a type of photoreceptor cell located within the retina, responsible for colour vision.
- Fovea: The fovea is a depression in the macula, which is the structure at the centre of the macula.
- Macula: The macula is a part of the eye located in the middle of the retina that is responsible for central vision.
- Rods: Rods or Rod cells are a part of the retina responsible for vision in low light.
- Photoreceptors: Photoreceptors are light-sensitive cells in the retina, responsible for turning light into electrical signals to send to the brain.
- Peripheral Retina: The peripheral retina is the part of the retina outside of the macula, responsible for peripheral vision.
1. Cones
Cones are a type of photoreceptor cell found in the retina. The purpose of a cone cell is to perceive colour, and fine detail and provide a person with colour vision.
2. Fovea
The fovea is a depression or pit in the macula, which is located within the retina structure. The macula is located in the middle of the retina, with the fovea located within the macula. It is where the cone cells, which help a person see colour vision, are located.
3. Macula
The macula is a part of the retina responsible for central vision. The macula is located in the middle of the retina and is responsible for processing what the eye sees directly in front, known as central vision.
4. Rods
Rods are a type of photoreceptor cells found in the retina, responsible for vision in low light. According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, rod cells are light sensitive and help better see in low light conditions, such as at night. Rod cells are found in the outer edges of the retina.
5. Photoreceptors
Photoreceptors are a type of light-sensitive cell found in the retina. The purpose of photoreceptor cells is to help transform light the eye sees, into electrical signals to send to the brain, which are then seen as images.
6. Peripheral Retina
The peripheral retina refers to the part of the retina outside or surrounding the macula. According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, the peripheral retina is responsible for peripheral vision.
How Does the Retina Help the Human Eye See?
The retina helps the human eye see by turning the light the eye sees into electrical signals that are sent to the brain. These signals are then interpreted by the brain as visual images. Different parts of the retina are responsible for different parts of sight, with the macula responsible for central vision and the peripheral retina responsible for peripheral vision. Photoreceptor cells within the retina, also help the human eye see, including cone cells that help the eye see colour, and rod cells that help the eye see in low light levels.
Is the Retina Sensitive to Light?
Yes, the retina is sensitive to light. The retina is a layer of light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye that turns the light that enters the eye into electrical signals to send to the brain, via the optic nerve.


Is the Retina the Most Commonly Damaged Part of the Eye?
The retina is not necessarily the most commonly damaged part of the eye. However, certain eye conditions that involve damage to the retina are common. Age-related macular degeneration for example is a common eye condition in which damage to the macula cells, which is the central part of the retina, causes central vision loss.
Can Stress Cause Retina Problems?
Stress may contribute to the development of eye conditions that affect the retina, but will not necessarily directly cause retina problems. Stress refers to a mental or physical strain and tension caused by pressures such as work, personal relationships and difficult situations. High levels of stress for prolonged periods of time can have a negative effect on mental and physical health.
What are the Different Ways to Take Care of the Retina?
The different ways in which a person can take care of the retina mostly revolve around caring for the overall health of the eye and the general body. The ways to take care of the retina and maintain eye health include attending eye tests with an optometrist, eating a healthy and balanced diet, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking. The ways to take care of the retina are listed below.
- Attending eye tests with an optometrist: Attending eye tests with an optometrist is an important step in caring for the macula and overall eye health. During an eye test an optometrist assesses a person’s vision and examines the structures of the eye including the retina. If there is an issue with the retina, an optometrist will be able to detect this, and provide the appropriate treatment.
- Eating a healthy and balanced diet: Eating a healthy and balanced diet is an important step for helping to take care of the structures of the eye, including the retina, and a person’s overall health. Eating a healthy and balanced diet includes consuming leafy greens, omega-3, fruits and vegetables, which helps provide the body with important vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin A and vitamin C. These vitamins can contribute to maintaining good eye health.
- Exercising regularly: Exercising regularly is an important measure to take in caring for overall health, which can contribute to good eye health. Exercising regularly involves participating in activities such as going to the gym, playing sports or running, which helps maintain weight and reduces the chances of developing certain diseases.
- Quitting smoking: Quitting smoking is an important way to take care of your overall health, as well as the eyes and the retina. According to the University of Michigan, Michigan Medicine, smoking can increase the risk of developing age-related macular degeneration, which is a structure located within the retina.
What is the Role of an Optometrist in Taking Care of the Retina?
The role of the optometrist in taking care of the retina is to provide eye tests that diagnose any issues with this structure and to provide treatment if said issues arise. An optometrist will take care of the retina by conducting an eye test, in which your vision is assessed, as well as examine the structures of the eyes for issues. The optometrist will assess the health of the retina during an eye test and determine if there is anything abnormal about it. If the optometrist finds any potential problems, they will treat and help manage them.
What is the Importance of a Regular Retinal Exam?
Regular retinal exams hold significant importance as they allow an optometrist to keep track of the health of your retina and determine if any issues need treating. A retinal exam may involve a fundoscopic exam or an ophthalmoscopic exam, which gives an optometrist a detailed look at the retina to assess its health.
How Can Oscar Wylee Help Take Care of Your Eye?
Oscar Wylee can help take care of your eyes, including the retina, by providing eye tests. Oscar Wylee optometrists are highly trained and passionate eye care professionals who provide eye tests in-store. Book online or visit one of our stores, and our optometrists can assess your vision and assess the health of the eye structures, including the retina, to determine if there are any issues that need addressing.
Can You Still See Without the Retina?
If there is significant damage to the retina, such as retinal detachment, it may be hard for a person to see properly. The retina is a light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eye that transforms light that the eye sees into electrical signals to send to the brain. The retina plays a crucial function in vision, and with significant damage, this may affect how well a person's vision works.
Does Wearing Eyeglasses Help Protect the Retina?
Wearing eyeglasses does not typically help to protect the retina, as the primary use of eyeglasses is to correct vision issues such as astigmatism, myopia and hyperopia. There are however several types of glasses that can help to protect the eyes and in turn the retina. The use of sunglasses, whether prescription or non-prescription, will help to protect the eyes from UV rays emitted from the sun. Safety eyewear such as goggles will also help to protect the eyes from injury.
Does Using Eye Drops Help Treat Retina-related Eye Problems?
There is emerging evidence that suggests eye drops may help with the treatment of retina-related eye problems such as retinal vein occlusion. According to the National Eye Institute, a study conducted on mice, carried out by Columbia University, concluded that eye drops may be more effective in treating retinal vein occlusion than the standard anti-VEGF injections typically used to treat this condition.
Can the Retina Heal Without Surgery?
Certain retina-related eye problems may be fixed without surgery, using methods such as injections or eye drops. However, surgery is a common treatment for many retina-related problems. In cases such as a macular hole or retinal detachment, surgery will be needed to fully repair the retina.